
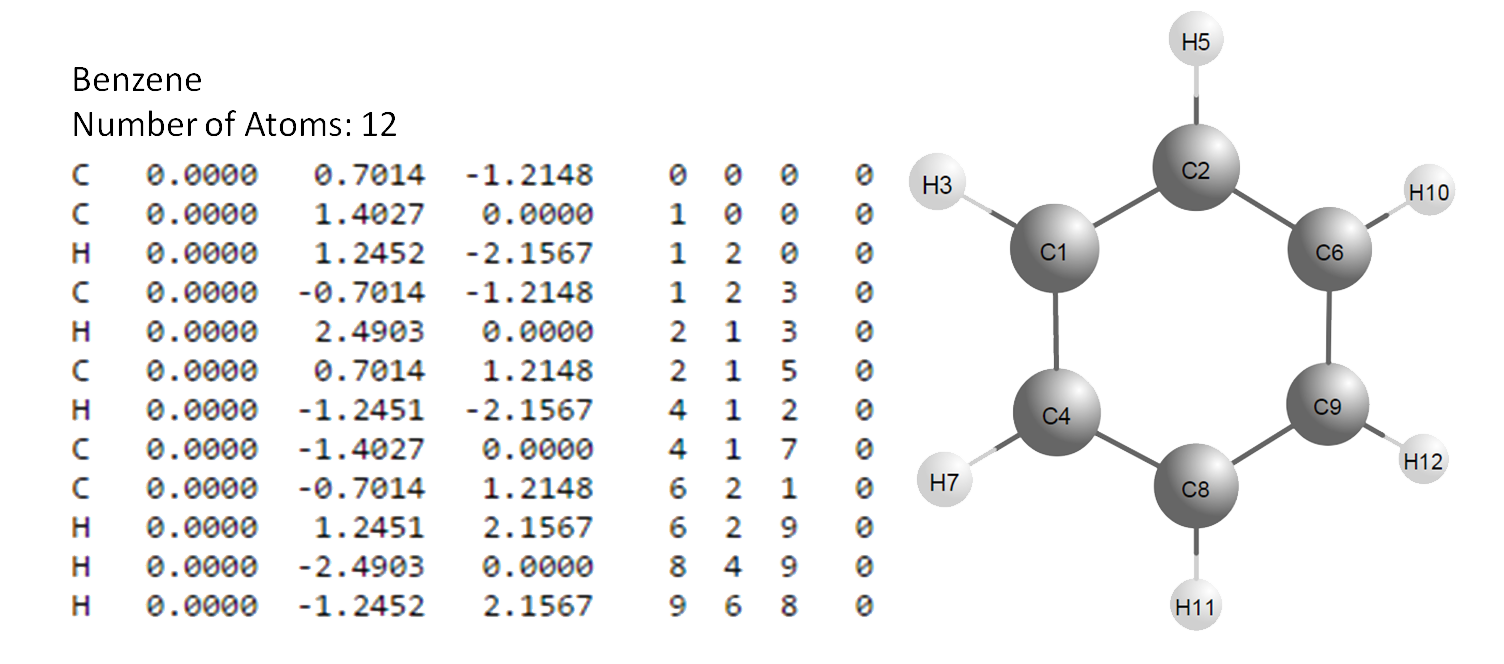


The Z-matrix provides a description of each atom in a molecule in terms of the internal coordinates Internal coordinates: Species of each atom Distances Angles Torsion (dihedral) angles This is particularly useful when working with molecular systems or restricted optimizations (control optimization variables) The name arises because the Z-matrix assigns the second atom along the Z-axis from the first atom, which is at the origin.Įxamples of the Z-matrix input in Siesta %block Zmatrix molecule This specifies the atoms that make up each molecule and their geometry.Įxamples of the Z-matrix input in Siesta In addition, an option may be passed, that indicates the units in which distances are specified in %block Zmatrix molecule fractional %block Zmatrix molecule scaled %block Zmatrix molecule In the absence of such an option, the distance units are taken to be the value of “ZM.UnitsLength”Įxamples of the Z-matrix input in Siesta %block Zmatrix molecule Nspecie i j k r a t ifr ifa ift One line per each atom in the molecule Double precision Integers IntegersĮxamples of the Z-matrix input in Siesta %block Zmatrix molecule Nspecie i j k r a t ifr ifa ift One line per each atom in the molecule Double precision Integers Integer flags that indicate whether r, a, and t, respectively, should be varied in a relaxation or molecular dynamics 0 for fixed, 1 for varying.
ZMATRIX DOWNLOAD HOW TO
Introducing the coordinates in Z-matrix form Objectives study how to introduce the coordinates of a molecule in Z-matrix form


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
